China In Spite Of Being In Illegal Possession Of Indian Territory Rakes Up Aksai Chin In UNSC
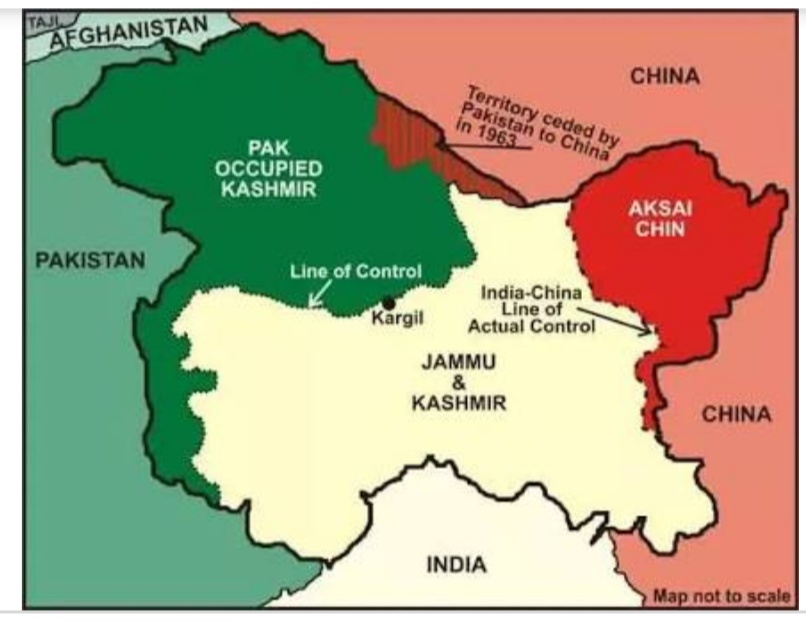
China not only supported Pakistan on the Kashmir issue at last Friday’s closed-door informal session of the UN Security Council, but also raked up the status of Aksai Chin, a territory in Ladakh illegally occupied by Beijing.
The Chinese Permanent Representative in the UN claimed that the government’s decision to abrogate Article 370 challenged China’s sovereign interests and violated bilateral agreements on maintaining peace and stability in the border area.
Luckily for China , there was no Indian Rep or Tibetan Rep present there to draw attention of everyone on illegal occupation and subjugation of Tibetan people. Also illegal occupation of Indian territory of Ladhak and Shakshagam area of Gilgit. China has also violated Indian sovereignty by its action in POK in the guise of CPEC.
“What should be pointed out is that India’s action has also challenged the Chinese sovereign interests and violated bilateral agreements on maintaining peace and stability in the border area and, on that, China is also very much seriously concerned,” the senior Chinese diplomat is believed to have said, in an indirect reference to the status of Ladakh. “And, we wish to emphasize that such unilateral practice by India is not valid in relation to China and will not change China’s exercise of sovereignty and effective administrative jurisdiction over the territory.”
Beijing decided to raise the issue at the UN despite Foreign Minister S Jaishankar allaying fears that re-designating Ladakh as a Union Territory would not impact the Line of Actual Control (LAC) and that Delhi was not making any additional territorial claims with regard to China.
During the bilateral foreign minister-level meeting in Beijing last Monday, Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi brought up the issue of legislation passed recently by Parliament on Jammu and Kashmir. Jaishankar told Wang that it was India’s internal matter. The issue relates to changes in a temporary provision of the Constitution and it is the sole prerogative of the country, he informed Wang.
The legislative measures were aimed at promoting better governance and socio-economic development. There was no implication for either the external boundaries of India or the Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China, Jaishankar told Wang.
Jaishankar also conveyed to his Chinese counterpart that so far as the India-China boundary question was concerned the two sides had agreed to a fair, reasonable and mutually acceptable settlement on the basis of the 2005 Political Parameters and Guiding Principles.
Pakistan has also ceded territory in Pakistan Occupied Kashmir to China, making Beijing a stakeholder in the occupied area.
ET has further learnt that the senior Chinese diplomat also raised the issue of human rights violation in Kashmir. This comes at a time when Beijing is facing serious charges of human rights violation in Xinjiang, Tibet and, most recently, in Hong Kong.
“It is ironical that a nation that has a chequered history of human rights violations in Tibet, Tiananmen, and currently in Xinjiang and Hong Kong, has sought to comment on the human rights situation in Jammu and Kashmir,” a source familiar with the developments said.
China has, so far, burnt its fingers twice this year while trying to safeguard its “all-weather friend” Pakistan at the UNSC.
Earlier this year, China was isolated while trying to protect Masood Azhar from being declared a global terrorist under its 1267 committee, but later backtracked.
Last week, China’s stature as a global power received a further jolt when no other country, except the UK, supported it at the UNSC on the issue of Kashmir. “This reflects the status China commands in the international community. Status is always not determined by raw power alone,” a source pointed out.
Though UK minister has now denied backing China or Pakistan on the issue.




